Common Yoga Protocol for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yoga and Diabetes
Evidence Base – Yoga for Diabetes
The Pancha Koça model to fathom the total human system and the concept of ädhi and vyädhi to understand the root cause of diabetes offers a strong scientific basis for the Holistic approach in health care delivery systems to be developed. A common general medicine cannot be administered to all ailments. Research through around 30 randomized controlled diabetes, 10 systematic reviews and five meta-analyses has shown yoga based life style change is better than exercise based life style change (Figure 1). Yoga based lifestyle modification helps in prevention and management of Diabetes
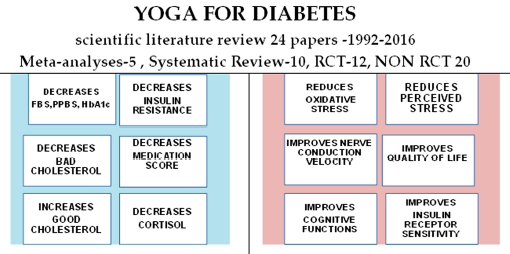
Figure 1: Summary of Researches on Yoga and Diabetes
What is the cause of diabetes?
Amongst many causes for different types of diabetes, type 2 is known due to a major factors. (a) the non- modifiable- the genetic factor; certain ethnic groups, such as South Asians, Pacific Islanders, Latinos, and Native Americans are genetically prone for diabetes. This seems to be due to enhanced sensitivity to the rapidly changing urbanization. (b) The modifiable cause is the lifestyle. Wrong lifestyle consists of four major factors – wrong diet, lack of physical activity, wrong habits and emotional tension, all trace-able to the mind.
Why life style is disturbed today?
Many scientific studies have proven that ‘Life style change’ is the cheapest and the most ef-fective method to prevent rapid progress of diabetes and its complications. The year 2002 was declared by WHO as the “year of non-communicable diseases”, to combat diabetes and heart diseases through life style change by emphasis on promotion of regular physical activity, non-smoking, and changes in diet. Continued efforts by policy makers at global level through declarations, awareness programs, education through the media etc seem to have no impact on the increasing rise of the curve of life style diseases.
What could be the reason?
Before the industrial revolution healthy life style was practiced and enjoyed fully as a part of cultural and religious practices. When spiritual growth of an individual formed the basis of the norms that were laid down for a social order, it was not difficult for the individual to accept restrictions on the temptations of the lower instinctual materialistic mind. But ever since the industrial revolution when the material affluence took the lead over spirituality, the scientists started disconnecting science from spirituality. What we are seeing today is a reflection of this attitude of those scientists who dispensed with consciousness, spirituality, God, faiths and belief systems and developed a mechanical model of the human body that was compared to a man-made mega machine ignoring the role of mind, the subtlest and the most powerful controller of human behavior. This has paved way for many of the life style related chronic ailments. Thus, it is obvious that the life style change requires a major change in the mind set of people. Yoga offers many tools for mind management.
Life style change through mind management is the solution that would take us forward in prevention and management of diabetes. Inability to handle the powerful mind is obviously the cause for disturbed life style. Let us understand what is mind and what aspect of the mind is the problem? Mind does thinking; We go on thinking continuously from the time we wake up until we go to sleep. What are the types of thinking we do? The four components are: grasping (perception), understanding (analysis), memory (registering and retrieval) and emotions (happy and unhappy). Emotions are a very vital component of our life. We do everything in life to get happiness and / or avoid unhappiness. All unhappy (negative) emotions are violent and distressful emotions which release lot of chemicals in the body. These chemicals are useful only when they are used for protecting the system during short term demanding situations of life. But these substances could damage the system when the emotions become long standing and persistent.
Yogic understanding of stress
Stress is not always a disease. Stress is a necessary response that helps us to cope up with a demanding situation and not the situation. The first response to perceived danger (physical or mental) is anxiety, or fear, an emotional response; this triggers increased activity in several parts of the brain and all organs of the body. To supply more energy for all cells to do their job better blood glucose has shoot up. The first response is in the mind- the fear and tension; this stimulates the activity of the emotional cortex, the limbic cortex; from there the activity comes down to the hypothalamus which is the stress button; chemicals are released; the nervous system is activated ; this in turn activates the adrenal gland, stimulates the liver, increases blood glucose in the blood. These responses are very essential for us to cope up with the demanding situation. Once the demanding situation is over, all functions return to normal.
As it happens in the present day lifestyle there are too many of these emotionally challenging situations. We have no time for the system to come back to normalcy and that is what gets stabilized over a long period of time. The persistent long standing responses which do not return back to normal is the problem. Thus, the anxieties, tensions, long standing worries, suppressed over a period of time becomes a habit. The part of the nervous system that has to restore normalcy has forgotten to do its job. This shows up as persistently high blood pres-sure or blood sugar or muscle spasm.
Therefore stress is a response and not the actual situation. During emotions the thoughts in the mind pick up enormous speed and go on rewinding. Thus all stresses are persistent emotions which are nothing but uncontrolled violent repetition of sentences in the mind.
Yogic understanding of diabetes as a mind body disease
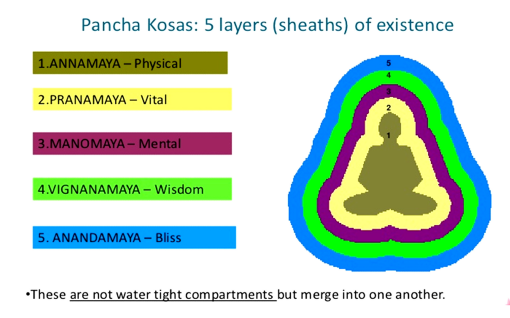
Once personality is not just a physical body that we see; it is made of 5 aspects – the annamaya kośa, prāṇamaya kośa, manomaya kośa, vijṇanamaya kośa and ānandamaya kośa.
In ānandamaya kośa, there is absence of all miseries; we are blissful with complete inner freedom. At this state there cannot be any illness because it is a state where the system is in perfect balance and established in blissful awareness even while at work. The lower mind that goes on changing with conflicts, craving, and desiring is called the manomaya kośa. There is a deeper aspect of the mind which has the right knowledge to sense what is right and what is wrong. When a person is tuned to the vijṇanamaya kośa, the actions will be in tune with cosmic laws, in tune with nature – no desires and therefore no misery, no disease. In the manomaya kośa actions are controlled by emotions and not by what is right or wrong. The strong long standing emotions in the manomaya kośa lead to persistent emotions, the stresses, called ādhi. Thus the diabetes, a life style disease begins in manomaya kośa.
The persistent long standing suppressed emotions percolate into the prāṇamaya kośa. The prāṇa, the life energy which is the subtle energy required for all bodily functions has to be in perfect balance with a harmonious flow. prāṇa flows through energy channels to supply right quantity of prāṇa to keep every cell healthy and happy. The harmonious flow of prāṇa gets disturbed due to activated ādhi at manomaya kośa. Over a period of time this excessive prāṇa settles down in the physical body, the annamaya kośa. annamaya kośa is the physical body that constitutes the anatomical structure-the cells, tissues, organs, all chemicals,
It is so evident to see the tremendous benefits obtained by the patients of T2DIABETES in such a short time by adopting integrated modules of Yoga for T2DIABETES treatment in centers.
hormones, nervous system etc. the physical body is a conglomeration of atoms ,protons and neutrons which in turn can be called quantum pockets of energy. The speed and violence that started in the mind and passed through the prāṇa, now manifests as speed in the body- the inflammation in the cellular level. This causes persistent cell wall problems resulting in insulin resistance.
Today, we know that pre-diabetes or diabetes with all the biochemical abnormalities is the result of inflammation. Inflammation in the cell wall in all organs is the cause of diabetes, Thus the problem is disturbed balance resulting from involuntary, uncontrolled speed-ed up long standing repetition of sentences in the mind over a period of time. Thus yoga offers a reversible model of diabetes as a mind- body disease.
Yoga based life style change for prevention and treatment of diabetes
As diabetes is a multi organ disease that begins in the mind and percolates through prāṇa to settle down as diabetes, it needs multi faceted approach to correct the imbalances. Thus the module of yoga includes yogic diet, exercises, āsana, praṇayāma and meditation apart from life skills through yama and niyama, jnāna Yoga, bhakti Yoga and karma Yoga to manage the mind to be able to adhere to healthy life style with contentment and joy.
Yogic diet
Eating is totally a psychological phenomenon in man due to the development of the higher aculties of awareness and mastery. So the mind uses appetite and satiety centers in the brain to offer the experience of fullness and emptiness. But when the mind is disturbed due to depression or uncontrolled desire, these do not work and the person ends up with problems of either obesity or under weight.
sātvika diet is a regimen that places emphasis on seasonal foods, fruits, nuts, seeds, oils, ripe vegetables, legumes, whole grains, and non-meat based proteins. sātvika diet described in Yoga literature in medieval era is mitāhara which literally means moderation in eating.
Both ancient and modern scientific literature shows that simple kitchen based herbs are found to be highly useful in diabetes control. Some of these herbs have been proven to have hypo-glycaemic and cholesterol lowering effects. They are from daily kitchen items in India and are easily available.
Exercise for Diabetes
Exercise is the only friend for insulin. The poor efficacy of insulin leads to inability of glucose to enter into the cells. Exercise is the best way for the poorly effective insulin to transport glucose from the blood into the cells. Exercise helps in reducing obesity and therefore the insulin resistance. Research has shown that moderate physical activity performed regularly for 120-200 minutes per week helps people to prevent diabetes. If you are a thin diabetic, then also physical activity is very useful and necessary.
This module of Yoga, includes śitilīkaraṇa vyāyāma in the beginning of the one-hour program, which has exercise effect. These śitilīkaraṇa vyāyāma or loosening exercises include simple trunk movements which prepare the body with better flexibility to move on to sūryanamaskāra. śitilīkaraṇa vyāyāmas followed by sūryanamaskāra offers the workout which is necessary to burn out the calories and transport more glucose from blood into the cells so that the muscles can spend away the glucose in a healthy way .
Three important points to remembered while doing Çithilékaraëa Vyäyäma:
a. Rhythmic movement which starts slowly and becomes faster,
b. Movements combined with breathing,
c. Deep internal awareness of the parts that are stretched.
Sürya Namaskära is a very interesting program which is a bridge between loosening exercises and the Yoga Äsanas. Sürya Namaskära is a combination of 12 Äsanas postures and to be performed like an exercise. During Sürya Namaskära three important points needs to be remembered.
a) sūryanamaskāra is done initially with fast movements, then performed slowly so that initially while performing rapidly, it will burn out calories involving muscles all over the body and when slowed down, one starts developing deeper awareness.
b) Combination of breathing with body movements is the most important component as it promotes concentration and complete body awareness.
c) sūryanamaskāra involves mind and emotion through devotion to sun. In the mind, one must have a continuous divine mood that ‘I am offering my salutation to the divine source, the Sürya, the Sun’. Therefore in the mood of offering, the mind becomes soft and gentle.
āsanam for Diabetes
In the first module, very simple but effective āsanas have been included. āsanas are not really exercises although they appears like exercises. The purpose of using the body movements in Yoga Äsanas is totally different.
āsana is defined as ‘sthira sukham āsanam’. Maintained in the final posture for a long time, it should become easy, effortless and enjoyable. They do not burn out calories but help to conserve calories. Therefore it works in harmony with nature and offers rest to the local stretched parts of the body. There are two aspects to experience while doing Äsanas. Sthira means maintain steadily for a long time, sukham means enjoy.
praṇayāma for Diabetes
praṇayāma means mastery over praṇa. Patanjali defines praṇayāma as slowing down of breathing . Breath in slowly and breath out slowly is praṇayāma. By slow breathing we can calm down the mind.
Mastery over all mental (Mmanah, chitta) and physical activities (praṇa) is health. Sickness is uncontrolled excessive praṇa. During stress, due to increased speed of mind, the habituated drawing of excess praṇa results in imbalance and blockages in the nādi disturbing healthy functioning of the chemical processes in the tissues ; thus the tissue damage (in annamaya kośa) is due to this excess persistent excessive flow of praṇa. So the aim should be to reduce the flow to the sick organ where the praṇa is locked up .This is achieved by doing cleansing type of breathing practice as in kapālbhāṭi followed by praṇayāma (slow breathing)-so slow that the breathing comes to almost 2-6 breaths / min.
Several types of praṇayāma techniques that may involve fast breathing, sectional breathing, uni-nostril breathing, alternate nostril breathing, with or without breath holding are all meant to achieve mastery over the praṇa and correct the imbalances.
Meditation for Diabetes
dhāraṇā, dhyāna, samādhi and devotion (bhakti) practices use the mind itself as the tool to control the mind and hence considered as direct (intrinsic) methods of yoga. dhāraṇā intensely is the first step in training. In the next step called dhyāna you learn to stay in effortless focusing. The benefit of this training is a direct mastery over the mind. Thus, an effortless easy flow of a single thought with slowness is the feature of dhyāna. Both dhāraṇā and dhyāna are practiced by using the picture of OM.
dhāraṇā and dhyāna also helps to deepen the effects of āsanas practices. For example, while maintaining in the final posture of vakrāsana focus on the painful, maximally twisted and stretched part of the back. and then let go the effort in the same spot (dhyāna) and feel the deep internal expansion, and slowness in that part. Thus, using this principle of focusing and de-focusing while maintaining in vakrāsana provides very deep rest to pancreas and abdominal fat improves the blood supply enabling the natural rejuvenating processes to be activated.
Bhakti Yoga for Diabetes
Another major practice at the manomaya kośa is devotion. Devotion or Bhakti yoga is a very easy trick to soften the violent emotions (either suppressed or expressed) that constitute any form of stress. It may be a reaction of anger, fear, jealousy, hatred, or depression triggered by demanding situations (external or internal). These negative emotions release large amount of stress hormones and contribute to bad control of blood glucose levels. Bhakti Yoga, the science of divine love, provides the knowledge base as well as a systematic training to soften these emotions. Regular practice of soft emotions such as pure love, compassion, pardon, peace etc. goes a long way in changing the pattern of reactions to situations. Bhakti is defined in Narada Bhakti Yoga sutra, as ‘parama prema rūpa’. Love is inborn even in animals. To love means to give. Giving and sharing is the feature of love. Regular practice to nurture intense love for personalized divinity through ‘giving and giving’ is the path. Surrender is the trick that takes away all stresses. Total surrender dissolves the ego to the extent that one starts experiencing the universal love. It helps one to mature and accept life as a gift and blessing from the beloved master. This forms the basis of life style change.
jnāna Yoga for diabetes
The knowledge base of spiritual health provides techniques that use the intellect to reach the state of yoga (complete freedom). One of the models prescribed in Upanishads is “Analysis of Happiness”.
This process of analysis used in Jïäna Yoga helps in complete mastery over cravings. Weight reduction and blood sugar reduction becomes easier. The severity of hunger pangs dies down and the urge for frequent eating goes away. The requirement of frequent doses of insulin reduces. The dose of the oral tablets also reduces.
Self management of stress at work
Occupation related stressors are the major causes of stress. Karma yoga is the practice that trains in working without getting worked up.
The tricks suggested in yoga texts include several conceptual inputs which can shift the mind from distressful reactivity to blissful activity. The hints of karma yoga include.
a. The art of working in relaxation
b. work with an attitude of Yajïa (offering to Divine)
c. Work without worrying about the results of action
d. Work with a sense of duty.
e. Live in the present.
f. Work in tune with the universal principle.
g. Begin the work for the joy of working and not for its reward.
h. Work with awareness. Make two compartments in your mind. Start working with full vigor in the outer; be established in peaceful silence in the inner compartment.
i. Recognize that this inner compartment of Änanda, the silence is your true nature. This is your soul. We are basically made of the universal stuff called Änanda from which the entire universe has emerged.
j. Realize that all pain and suffering, losses, and gains in business, name, fame and money including the physical body are all ephemeral; that they all come and go and ‘you’ are the ever-lasting, unchanging, ever blissful, imperishable entity.
Thus, the yogic life style change includes not only the high fiber, low carbohydrate, zero fat vegetarian food and regular exercise, but it goes into the deepest personality to motivate and adhere to healthy and blissful life style under all circumstances.
All about the Common Yoga Protocol for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Syllabus - Practice Topics
-
Locate Centers
Common Yoga Protocol for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
(Total duration of 60 minutes: 30 minutes of Physical Activity; 30 minutes of prāṇayāma + Relaxation; to be practiced at least 5 days a week)
| S. No. | Name of Practise | Duration |
| 1 | Starting Prayer: Asatoma Sat Gamaya | 02 Minutes |
| 2 | Preparatory Sukshma Vyayamas and Shithililarana Practices 1. Urdhvahastashvasan (Hand Stretch Breathing 3 rounds at 90°, 135°, 180° each) 2. Kati-Shakti Vikasaka (3 rounds each) Forward and Backward Bending a. | b. Twisting 3. Sarvangapushti (3 rounds clockwise, 3 rounds anti-clockwise) |
06 Minutes |
| 3 | Surya Namaskara (SN) a. 10 step fast Suryanamaskara 6 rounds B. 12 step slow Suryanamaskara 1 round (To be avoided by those with knee pain, cardiac problems, renal problem, low back pain, retinopathy and the elderly who are weak and not flexible; instead they can do Chair SN) Modified version Chair SN: 7 rounds |
09 Minutes |
| 4 | Asanas (1 minute per asana) 1. Standing (1 minute per asana) Trikonasana, Pravritta Trikonasana, Prasarita Padhastasana 2. Supine Jatara Parivartanasana, Pavanamuktasana, Viparitakarani 3. Prone Bhujanagasana, Dhaurasana followed by Pavanmuktasana 4. Sitting Mandukasana, Vakrasana /Ardhamatsyendrasana, Paschimatanasana, Ardha Ushtrasana At the end, relaxation with abdominal breathing in supine position (vishranti), 10-15 rounds (2 minutes) |
15 Minutes |
| 5 | Kriya a. Agnisara: 1 minute | b. Kapalabhati (@ 60 breaths per minute for 1 minute followed by rest for 1 minute) |
03 Minutes |
| 6 | Pranayama a. Nadishuddhi (for 6 minutes, with antarkumbhaka and jalandhar bandha for 2 sec) b. Bhramari (3 minutes) |
09 Minutes |
| 7 | Meditation (For stress management for deep relaxation and silencing the mind) Cyclic Meditation (Those who are willing to practice techniques of relaxation evolved by their own institutes may do so) |
15 Minutes |
| 8 | Resolve (I am completely healthy) | 01 Minute |
| 9 | Closing Prayer: Sarvebhavantu Sukhinaha… | 01 Minute |